Keto Weight Loss Diet: How Does It Work?

Keto weight-loss diets are a rage all over the world. From cheesy breakfasts and meaty dinners, could a diet ever taste better? But how does keto really promote weight loss, and at what cost?
You have obviously heard about the keto weight loss diet, and possibly even know a fair bit about it already. It isn’t a diet. It’s a fitness celebrity in its own right.
Keto is extremely famous and thrives mostly on social media. Most “fit influencers” social media pages have been a vortex of Ketogenic-photogenic. Before and after, keto-diet photos. Delectable keto-diet food photos. My royally-rich ketogenic dinners photos.
These are literally the first dieters in known history who make you wish you were on their diet. Honestly, how did the world come to eating glistening steaks and melting strings of cheese while on diet?
We are here to tell you every bit of the why and how of it.
What is a keto weight loss diet?
Everywhere in the world, a traditional meal looks carbohydrate-centric. It is hard to find even a single place in the world where the “staple food” isn’t one heap of carbs. Bread, rice, potatoes, pasta, noodles, etc. sit bang in the middle of every plate in the world.
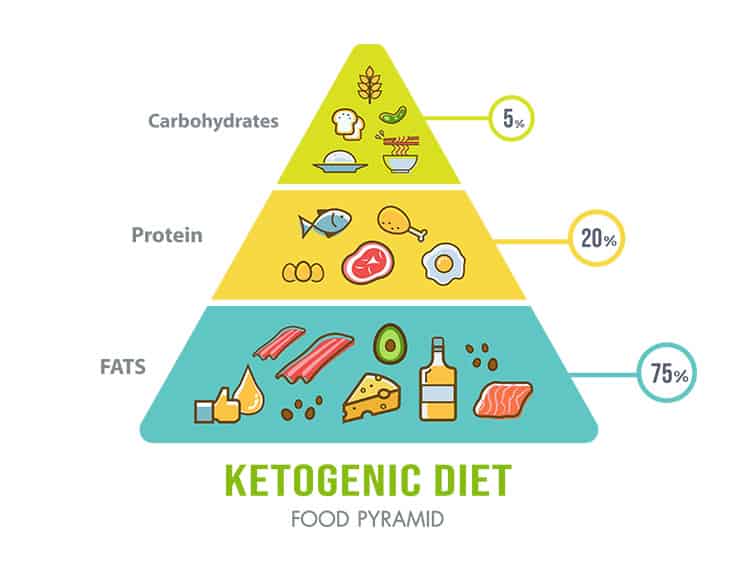
Keto turns this eating pattern on its head. In a ketogenic diet, you consume little or no carbs, some protein, and lots of fats. A macronutrient pyramid of a standard ketogenic diet is comprised of 3-5% healthy carbs, 20% proteins, and 75% fats. Here is a pyramid graph representing the same:
Origins of keto
Let’s discuss its workings inside our body in detail but before that let’s take a quick look at its history. How weird is it that we are drooling over a weight loss diet that was originally invented as a treatment for Epilepsy [1]News Medical Life Sciences: History of the Ketogenic Diet!.
In 1972, Robert Atkins (sounds familiar?) published his book on the Atkins diet. His diet also centered on depriving the body of carbs to make the body burn off fat to generate energy.
The world rediscovered the Atkins diet in the 2000s. More studies popped up in the second decade of the 00s proving the benefits of artificially induced ketosis (don’t sweat over those terms yet). It didn’t take long for the drab, science-ey-sounding ketogenic diet to be crowned the coolest diet ever.
How does keto work for weight loss?
Consider the recommended number of calories for a person your age/height/weight/level of physical activity. Now think of the number of carbs, proteins, and fats you are allowed to consume to achieve your required number of calories. Keto diets flip that ratio on its head.
Here is a table for some perspective:
|
USDA | 55% CARBS | 20% PROTEIN | 25% FAT |
| KETO DIET | 5% CARBS | 20% PROTEIN |
75% FAT |
So how exactly does keto use this to promote weight loss?
Our bodies are rather ancient machines. Over millions of years of evolution, it modified the internal engine to deal with possible scenarios of starvation.
After all, food wasn’t easy to come by throughout most of our evolutionary history. Neanderthals couldn’t possibly order a packet of fries to their cave when going out for a hunt seemed impossible.
They would starve to death if the body hadn’t evolved Ketosis. It’s a flashy name for a system where the body squirrels away every bit of extra calories it gets per day as fat.
This fat gets stored in the liver. On low food days, the body digs into the reserve fats. The liver breaks them down into compounds called ketones. This is used to keep the body powered and running.
This is the mechanism that the ketogenic diet has hacked to promote weight loss. Keto diets cut down massively on carbs. The body’s primary source of energy.
A day or two in this state, the body assumes it is in a starvation situation and starts attacking accumulated fat reserves. See that? An effective fat-burning mechanism was inside your body all along.
Average weight loss on keto
Ketogenic diets have been observed [2]National Library of Medicine: Ketogenic diet for weight loss to have led to 4 pounds more weight loss in a year than low-fat diets. On average, people can start losing 1-2 pounds per week, once the body’s ketosis kicks in.
As easy as it seems to put the body 1-2 pound fat-burning mode with chunks of cheese and blobs of butter, the process is very fragile. There are two things to keep in mind:
- Ketogenic weight loss has been known to plateau after a certain amount of time. The weight loss stops after some time.
- The body stops ketosis the first moment it discovers that extra calorie. If you overeat anything or bite into one tiny hash brown, the body attacks it with vengeance. You will have to start all over again, and it will take a couple of days to restart the ketosis.
Keto diet food list
Here is a list of foods you can eat and the foods you cannot eat while you are on a keto diet:
|
What you can eat | What you cannot eat |
|
Fatty fish and all seafood |
Grains |
|
Cheese, Yogurt, cottage cheese |
Sweet yogurt |
|
Eggs |
Milk |
|
All poultry meats |
Sugar in any form |
|
Nuts of any kind |
Honey, or Syrup |
|
Natural oils and fats |
Juices |
|
Non-starchy, low-carb vegetables. |
Starchy, carb-dense vegetables |
|
Berries |
Fruits |
|
Tea and Coffee |
Baked foods |
| Dark chocolate, Cocoa. |
Chips, fries, and crackers. |
Source – Healthline
Divide the foods allowed into your diet according to the previously mentioned carb-protein-fat ratio. For our convenience let us assume the rough approximation of 2000 calories per day. Plan your meal such that you consume a combined 165 grams of fat, 75 grams of protein, and 40-50 grams of carbs.
Remember the cardinal rule. The numbers depend on you. Your physical vitals, stats, and your lifestyle. Be aware and modify the numbers accordingly.
Benefits of keto diet
- Weight loss, of course,
- Most people report that they feel less hungry when on a keto diet.
- Unsurprisingly, keto improves insulin sensitivity and controls blood sugar levels.
- Some studies have claimed that keto diet slows down the progression of some forms of cancer.
- A January 2013 study [3]Gladstone Institutes: Gladstone Scientists Discover Novel Mechanism by Which Calorie Restriction Influences Longevity found that powerful anti-inflammatory genes and antioxidants are released when you limit carb-based calories. This has the power to slow the aging of the mind and the body.
- Consequently, keto may have positive effects on the brain and its functioning in some people.
- Surprisingly, you might end up with lesser dental plaque too. After all, oral bacteria love your sugars as much as you do. Keto diets deprive you and your dental bacteria of those unwanted sugars.
Is keto safe for you?
The Keto diet has definitely had its share of controversies. Clearly, nature didn’t mean us to live carb-starved lives. Moreover, fat and protein-intensive foods cause specific kinds of strain on specific organs of the body. Here are a few potential risks a keto lifestyle might pose:
Heart Health Issues: All that fat-rich diet isn’t going to sit well in your heart. Keto has been linked to increased LDL, the bad cholesterol.
Liver Health Issues: The body’s excess fats are stored in the liver, which then breaks it down into ketones. With too much fat to metabolize, your liver can be strained. People with pre-existing liver conditions should be cautious of taking up a keto diet.
Kidney Health Issues: Kidneys process the protein we eat. There is a huge risk of nitrogen imbalance and kidney stones due to all the excess nitrogen excreted as urea.
Gut Health Issues: A ketogenic diet is unrealistically low on fiber because of its strict rules against carb intake. Fibers are, after all, a polymer of carbohydrates.
Fiber is important for healthy bowel movements. Without fiber, bowels stay longer in the intestine and putrefy. Keto diet followers often complain of a wide range of gastrointestinal problems ranging from constipation to diarrhea to hemorrhoids.
Mental Health Issues: The ketogenic diet was primarily introduced to help with a particular neurological issue: Epilepsy. The idea was to starve the patient of sugars to slow down some over-firing neurons. Unsurprisingly, when common, healthy people try the same diet they begin to experience mood swings, confusion, and irritability.
As much as we demonize both salt and sugar, our brains need them for some very basic neurological functioning. Keto diet deprives the body of every last bit of sugars, in every imaginable form. This is extremely dangerous to brain health.
Other problems of a keto diet:
- Keto diets are extremely difficult to stick to. The food looks extremely inviting initially, but we forget that it cuts out an extremely large variety of very basic foods from our diet.
- It causes nutrient deficiencies for the same reasons.
- “People do not exercise good judgment in choosing the right fats. Not all forms of fat are good even if your body is in ketosis”, finds a study [4]The University of Chicago Medicine: Ketogenic diet: What are the risks?.
- There is a danger of using the worst possible sugar substitutes. Since all healthy and natural forms of sugar are banned, people choose dangerous substitutes like sorbitol to satisfy their sugar cravings.
- Muscle cramps, and weakness.
Keto isn’t a very sustainable weight loss diet in the long run. If you wish to step on the keto bandwagon, make sure you have enough knowledge of this diet and a good source of guidance. A good doctor, dietician, or nutritionist will guide you into taking up the diet in the right way without leading to new health problems or worsening existing ones.
References
| ↑1 | News Medical Life Sciences: History of the Ketogenic Diet |
|---|---|
| ↑2 | National Library of Medicine: Ketogenic diet for weight loss |
| ↑3 | Gladstone Institutes: Gladstone Scientists Discover Novel Mechanism by Which Calorie Restriction Influences Longevity |
| ↑4 | The University of Chicago Medicine: Ketogenic diet: What are the risks? |







